#malign foreign influence
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
by Asra Q. Nomani
Another troubling example is the “Hands Off Uhuru Fightback Coalition,” whose leaders face charges in a Tampa court in September for allegedly working with Russian intelligence to interfere in U.S. elections. In a statement that rings true today, Matthew G. Olsen, assistant attorney general in the Justice Department’s National Security Division prosecuting the Uhuru case, said last year, “Russia’s foreign intelligence service allegedly weaponized our First Amendment rights – freedoms Russia denies its own citizens – to divide Americans and interfere in elections in the United States.” Assistant Attorney General Kenneth A. Polite, Jr. of the Justice Department’s Criminal Division called it “foreign malign influence.”
These groups are not merely focused on domestic issues; they harbor broader, international ambitions, for which they are willing to “disrupt the DNC,” even if it costs Harris votes – and potentially the presidency. Many of them seek to dismantle the current global order, with a particular focus on the Middle East and the destruction of Israel.
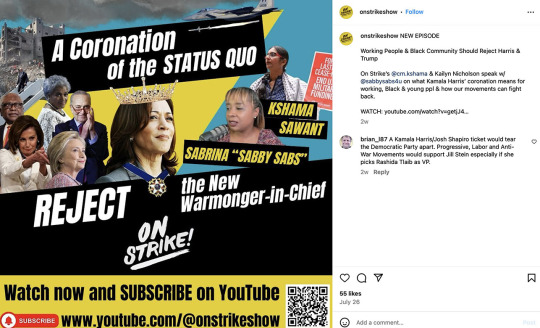
At the heart of this coalition lies a shared animosity towards the Democratic Party and, now, Harris. The Atlanta chapter of the National Alliance Against Racist and Political Repression tells its followers Harris is “funding genocide and ignoring police terror.” “Workers Strike Back” tells Americans to “REJECT the New Warmonger-in-Chief.”
By presenting the protests as “grassroots,” the media has underplayed the powerful forces behind controversial messages, like “HAMAS IS COMING,” during the network’s recent protests in D.C., when the American flag was burnt and replaced by the Palestinian flag. By not dissecting their motives, the media has also given them a powerful bullhorn. These protests are not spontaneous uprisings of concerned citizens. They are carefully orchestrated campaigns designed to subvert U.S. elections and undermine American democracy.
These protestors seek to overthrow the current political order, or as one organizer, “Socialist Action,” says: “Permanent Revolution.” Their demands are absolute, and their tactics are ruthless. Democratic Party leaders must recognize that there is no winning with these groups. Their aim is to tear down what exists and rebuild it in their own intolerant image.
Andrew Fox, a former British military officer who did three tours of duty in Afghanistan, tells me: “These protestors are not just demonstrating; they are fomenting an insurgency designed to destabilize the U.S. and further the interests of foreign actors.”
Democratic Party leaders and Harris would be well served to refuse to be swayed by the loudest voices on the streets, who pledge to “Disrupt the DNC,” as “Workers Strike Back,” supporting “Left Antiwar Independent Candidate” Jill Stein, threatens to do. Firebrand, a self-described “communist organization” and coalition member, has guided its members to avoid playing a game of “lesser evilism” and refuse Harris’s candidacy.
The fight against disinformation warfare is not easy, but it is necessary. By shining a light on the truth behind the myth of the marching millions, understanding details like who funds protests and rents charter buses to Chicago, we can make wise decisions, not misled by fear and chaos, but rather guided by transparency and facts.
13 notes
·
View notes
Text
Theory: Viktor engineers his way out of his Hexcore fate.
Or: How we may still get a Machine Herald Viktor
We see Viktor in Act 1, once creator of the Hexcore, now controlled by that which he once gave life to. Viktor, agency lost to a body now foreign to him and no longer entirely his own.

But in this teaser poster, we see Viktor looking conflicted, scared almost.

His hand covers his face, in the pantomime of a mask, like he’s conflicted over his identity. Viktor, grappling with the tug of war of the Hexcore’s influence, maligned with retained memories of a distant self.
I’ve been thinking about how they might reconcile the current version of him with his League counterpart (assuming Riot even still wants anything to do with the original lore).
I think we could still see Viktor reverse engineer his way out of his fate. Because Viktor is no stranger to being trapped in a body with physical limitations, a body which doesn’t always function the way he wants it to.
Imagine:
- Viktor, tearing himself apart in an attempt to remove the parasitic parts of the Hexcore.
- Viktor, surgically amputating part by corrupted body part, and replacing them with the certainty of steel and science.
- Viktor, reclaiming his agency from a transformation not entirely of his own volition, to a self made glorious evolution engineered by his own hands.
#arcane#viktor arcane#arcane viktor#viktor league of legends#arcane analysis#arcane season 2#arcane spoilers#jayvik#arcane headcanon#sicklyscientist
723 notes
·
View notes
Text
The target is you, voter. Russia, China, Iran, and other bad actors sought to interfere in the run-up to today’s US elections, according to research by the Atlantic Council’s Digital Forensic Research Lab (DFRLab), which has been monitoring online trends along with statements by governments, private companies, and civil society in its Foreign Interference Attribution Tracker. As DFRLab experts detail below, this year’s malign efforts in many ways surpass previous influence campaigns in sophistication and scope, if not in impact—and they are expected to continue well after the polls close.
Tipping the scale
“By sheer volume, foreign interference in the 2024 US election has already surpassed the scale of adversarial operations in both 2016 and 2020,” Emerson says.
Dina notes that each US adversary played to its strengths. For example, Iran and China “attempted to breach presidential campaigns in hack-and-leak operations that raise concerns about their cyber capabilities during and after the elections,” she tells us.
At the same time, the United States is more prepared than it was in previous election cycles. Russian efforts in 2016 “made foreign interference a vivid fear for millions of Americans,” Emerson notes. “Eight years later, the US government is denouncing and neutralizing these efforts, sometimes in real time.”
In fact, Graham tells us, “the combined actions by the US departments of Justice, Treasury, and State against two known Russian interference efforts was the largest proactive government action taken against election influence efforts before an election.”
Doppelgangers and down-ballot races
US officials this week called Russia “the most active threat,” and it’s easy to understand why. Emerson notes Russia’s “ten-million-dollar effort to infiltrate and influence far-right American media,” alongside the “Doppelganger” network, which has spread “tens of thousands of false stories and staged videos intended to undermine election integrity in the swing states of Pennsylvania, Georgia, and Arizona.” Increasingly desperate, Russian actors have even sought to shut down individual polling places with fake bomb threats, he adds.
Meanwhile, China has focused on “down-ballot races instead of the presidential election to target specific anti-China politicians,” Kenton explains. Using fake American personas and generative artificial intelligence, China-linked operations have appeared across more than fifty platforms. Perhaps surprisingly, Kenton adds, “attributed campaigns appeared sparingly” on the Chinese-owned platform TikTok and far more often on Facebook and X.
Faith, fakes, and falsehoods
“The primary aim is to erode Americans’ faith in democratic institutions and heighten chaos and social division,” Kenton explains, and thus to undermine the ability of the US government to function so it will have less bandwidth to contain adversarial powers.
“Some of the fake and already debunked narratives and footage circulating before the elections will likely continue to be amplified by foreign threat actors well after November 5,” Dina predicts. Expect to see activity around the submission of certificates of ascertainment on December 11, the December 17 meeting of the electors to formally cast their votes, and through inauguration day on January 20.
And in a post-election period where the results will likely be contested, Graham thinks there’s a “high likelihood” that foreign actors will “cross a serious threshold” from pre-election attempts to broadly influence American public opinion in service of their geopolitical interests to “direct interference” by trying to mobilize Americans to engage in protests or even violence.
Nevertheless, Graham points out that the high volume of foreign-influence efforts observed during this year’s election cycle so far does not appear to have had a significant impact in terms of changing Americans’ opinions or behavior.
The consequences of foreign disinformation, Emerson adds, should be assessed against “the far more viral, sophisticated, and dangerous election-day falsehoods that Americans spread among themselves.”
85 notes
·
View notes
Text
I want to argue that Dracula is the first work of Nokiawave.
-It's heavily concerned with new technology which drives the plot: Telegrams between everyone being collated into the text, Dr Seward's audiolog on the phonograph which Mina types up, mass transit in the form of both trains and Tube, steamships (and specifically the contrast between steam and sail) and loads of minor examples.
-It's concerned with new social technologies and social change: Mina is a typist, a respectable modern job for a young middle-class woman. Jon is a clerk and is working in an exciting emerging market. Dr Seward uses all the modern methods and keeps up with theory and scientific developments. Lucy is pleased to have plenty of male friends, not just to be seeking to marry. And it contrasts this with both the "good" Old Ways - The helpful, hopeless, peasants who give Jon his anti-vampire icon, the "broad minded" but also clearly steeped in superstition Van Helsing - and the "bad" Old Ways - Obviously, Dracula and also the enslaved Roma (Who, oh god, I I have to write about them in the context of Romanian chattel slavery of Roma, which was technically abolished in stages throughout the 2nd half of the 19th century, but where emancipation came with enforced sedentarism and obligation to a landowner - And where many remained enslaved in all practical terms into the C20th, and specifically in Transylvania the effects of Maria Theresia's Four Decrees that were still in effect that meant they would both be indentured to a landowner as "new farmers" and their children would be kidnapped by the state and given to white families for "reeducation" - but most people analysing the text seem to treat them as willingly Evil Minions).
-It's full of the anxieties about what Eastern and Southern Europe will do as they "modernise and open" (ie become financially and culturally available to the West) and specifically the fear of the Rich Slavic* Oligarch (to a certain kind of British mind, anyone east of Berlin and north of Athens is Slavic, sigh) spreading their malign influence in the Capital Cities of the West. Even the touch that Dracula was once a warlord but is now a slick investor and man-about-town.
-It has lots of continent hopping, focusing on the ~local colour~ in Transylvania and the contrast between both the "superstitious" locals and the traveller who finds it all very quaint and interesting but not very serious, and between the poverty of the normal people and the wealth and seclusion of Dracula, and then likewise giving us whistle-stop tours of the interesting bits of Whitby and London, making the city as much of a character as the humans. The Westerner abroad is seen as just a natural phenomenon, but the foreigners* in Britain are notable and exotic.
- It has a mysterious superweapon/monster which is hidden around a big western capital city, where most people (and even the police and regular military) have no idea what it is and are powerless to stop it, and a lot of tension lies on the crux of "What happens if this gets out here, surrounded by all these civilians?" - In a way that treats the mythological East* as a natural place for atrocities to occur, but them happening in London is a shock.
-It has spying: Jon sneaking around the locked-up Carfax with his miniature camera, trying to take pictures to find out what Dracula is doing in there, could have absolutely been in a 1990s thriller. Likewise, meeting in Harrods to avoid suspicion because it's a plausible place for a fashionable young lady to be, surrounded by anonymising crowds.
-It has information warfare: Dracula reading up on British politics, studying maps of London, paying clerks and using shell companies to disguise his property acquisitions, and likewise the heroes using the telegram and port records and the sheer mass of paperwork generated by his activities to track Dracula, which feels like close kin to the Nokiawave staples of finding someone on cctv or by their credit card, or their car registration being flagged at a checkpoint. Jonathan lamenting the lack of an Ordnance Survey in Europe and the unmapped bits of Transylvania specifically really fits with the idea of the "Control Grid" posited by Gregory Flaxman who writes a lot about surveillance and information control in cinema.
-It has a team of both specialists and laypeople who were dragged into the action by circumstance, and much relies on their relationships. The laypeople's "unimportant" skills (Jonathan's knowledge of property and finance especially, and Mina's skills with logistics as well as her innovation and bravery in using herself as a conduit to Dracula) turn out to save the day. The team is multi-national and basically represents The Free World (TM), as well as allowing for jokes about national stereotypes.
-Mina being notably not a damsel in distress, but instead using her personal connection to the villain to absolutely ruin him in ways that nobody else could, is very much like the role of many women in Nokiawave films: She may be traumatised and in danger, more than anyone else because of the villain's obsession with her, but she's smart and deadly and willing to take risks to complete the mission.
-It ends with a massive cross-continental vehicle chase with tonnes of explosions.
195 notes
·
View notes
Text
Cost-cutting is now the rage of Trump 2.0 and the dread of bureaucrats inside the Beltway. While rooting out malign foreign influence in higher education is one of the quieter battles taking place within the broader effort to tackle the national debt, Trump’s Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) offers an elegant and principled solution: taxpayers should not have to compete with totalitarians in university funding.
Far too often, American universities see themselves as cosmopolitan city-states positioned beyond the reach of constitutional law or American cultural norms. Unlike in a typical American workplace, anti-Semitism is tolerated on college campuses. In higher education, discrimination against competent Asian and White students is not considered racist, but is rather seen as a virtuous pursuit of “diversity, equity, and inclusion.” Topping it off, universities offer pricey degrees to students with little guarantee of job prospects and a crushing debt burden. For all of its talk of resisting Trumpian authoritarianism, America’s universities and colleges have eagerly accepted funds from countries like China, Russia, and Qatar while agitating for “Boycott, Divestment, and Sanctions” against Israel.
8 notes
·
View notes
Text
8 notes
·
View notes
Text

A panel of experts testified to the House Foreign Affairs Committee on Tuesday that Chinese companies mining for “green” energy minerals throughout Africa – particularly in resource-rich countries such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), are creating a “catastrophic and unacceptable” situation for locals.
The experts urged American officials to act to contain the malignant Chinese influence destroying an entire generation of African children and the environment in which they live, stressing that the minerals in question – cobalt, lithium, tantalum, and copper, among others – are pivotal to any high-tech economy.

The hearing, hosted by the Subcommittee on Africa and chaired by Rep. Chris Smith (R-NJ), occurred as the nation of Zambia struggles to address the virtual death of the Kafue River, drowned in toxic residue when a dam holding the residue, created through Chinese copper mining activities, collapsed. Among the specific environmental threats mentioned at the hearing were the threat to the endangered okapi and the destruction of entire communities, displaced by companies looking to mine the land and polluted to the point that no one can safely return.
In addition to environmental disasters, the growing presence of exploitative Chinese companies in the DRC, Zambia, Zimbabwe, and elsewhere has brought with it growing rates of child slavery as children as young as eight are forced into mines with no protective equipment, greatly endangering their lives. Furthermore, the mineral wealth and corruption is also fueling chaotic guerrilla warfare, particularly in the DRC, where rival militias regularly commit atrocities for control of the mines and violence has been exacerbated by Rwandan intervention. As of February, the death toll of the ongoing DRC conflict is estimated to be in the high thousands and the United Nations has documented a large number of instances of the use of rape as a weapon of war.

The issue of child slavery in the mines featured prominently during the hearing. Sasha Lezhnev, a senior policy adviser with the Sentry, stated that, in the DRC alone, “there are an estimated 25,000 to 35,000 child miners … working at mines that send cobalt and copper to Chinese crude refiners.”
“I have witnessed the horrors of child soldiers and child miners as young as eight years old at mines in the Democratic Republic of Congo,” Lezhnev shared, “as well as the warlords and corrupt companies and officials making money from this system of exploitation—all in the name of getting us cheaper smart phones, jewelry, and electric vehicles (EVs). This has got to stop.”

“We see cases of child and forced labor—averaging 40,000 children–digging cobalt for Chinese buyers without adequate protective equipment and payment,” Joseph Mulala Nguramo of the Atlantic Council Scowcroft and Freedom and Prosperity Center told the subcommittee. “Some of these children are under 10 years old—leaving them exposed to toxic substances—causing serious health and environmental problems, per Amnesty International investigations.” . Nguramo described the situation of those children, as well as the lives of locals in areas affected by Chinese mines generally, as “catastrophic and unacceptable.”

In the DRC, ongoing civil unrest and an unmitigated humanitarian crisis are largely due to China’s ruthless and irresponsible grip on the country’s natural resources,” Nguramo testified. “Controlling almost 90% of the Congo Mining Sector, China has failed to use its economic and financial power to defend and promote the Rule of Law, Freedom, and Quality Governance. But China has, instead, mastered strategies to take advantage of a country in chaos—often bribing government officials to acquire Mining concessions.”
The experts testified that China had spent over $10 billion buying up mines in Africa, benefitting the most so far in Zambia, the DRC, and Zimbabwe, though the Communist Party has significantly expanded its influence elsewhere in the continent, as well. The founder of the due diligence firm Accountable Africa, Thierry Dongala, noted that widespread corruption in local governments enables this colonialism and pointed to the example of Niger to show that African governments can rapidly expel offending Chinese companies if they choose to. Niger, currently under military coup regime that calls itself the “National Council for the Safeguard of the Homeland,” reportedly expelled Chinese oil executives from the country in mid-March and shut down a Chinese-owned hotel for allegedly engaging in “discriminatory practices.”

“The recent case of Niger expelling Chinese management shows that when African countries get serious about their moral sovereignty in their extractive industries, Chinese actors are often the first to lose,” Dongala observed.
Dongala noted that local populations are well aware of the evil that illicit, slave-driven mining brings to their land, recalling that the pastor who married him to his wife conducted a “sudden sanctification prayer” to cleanse their wedding bands of evil energy, a product of their provenance, when he noticed they appeared to be made of real gold. He recommended close cooperation with locals in affected countries to track and shut down theft, slavery, and other abuses.
“We’ve been monitoring the school attendance levels, that data is very valuable because we know that if we start to see the school attendance levels drops, we have to find where these kids are going,” he said of his firm. “The local school principal , the local fishers union, the mothers of the children,” he suggested, could be critical allies.
Rep. Smith, chairing the hearing, noted that China’s dominance of the mining industry there, in addition to facilitating unspeakable human rights and environmental atrocities, put America at a disadvantage given the importance of the minerals in question in technology.
“The reliance on China for these critical minerals is a clear vulnerability,” he emphasized in his opening remarks. “The greatest beneficiaries of this system—China’s state-owned mining companies—remain silent, refusing to confront an undeniable reality: from dirt to battery, from cobalt to cars, the entire supply chain is built on violence, exploitation, and corruption,” he continued. “This must change—and the time for change is now.”
Rep. Smith recently reintroduced the COBALT Supply Chain Act, a bill that would, in its own words, “ensure that goods made using or containing cobalt refined in the People’s Republic of China do not enter the United States market under the presumption that the cobalt is extracted or processed with the use of child and forced labor in the Democratic Republic of Congo.” Rep. Smith first introduced a version of the bill in 2023.
Progressives don't care about REAL slaves living today. Just remember that EV you're driving was built at the expense of 10 little African kids whose future was stolen in order to make the battery.
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Elon Musk’s Malign Influence in Brazil

At 11:02 a.m. Eastern Daylight Time on April 7, 2024, Elon Musk—billionaire investor, tech CEO, and would-be Imperator of Mars—posted on the social media platform he owns, calling for the judge who presides over Brazil’s powerful Superior Electoral Tribunal (TSE) to “resign or be impeached.” In Musk’s view, the judge, Alexandre de Moraes, was guilty of the high crime of censorship.
Days before, Substack author Michael Shellenberger reprised his Twitter files gambit in a post accusing the TSE of “anti-democratic election interference” and decrying the “birth of the Censorship Industrial Complex in Brazil.” The Republican-controlled United States House Judiciary Committee later released a sealed Brazilian Court order, apparently obtained by subpoena, showing that the TSE had ordered Musk to take down about 150 accounts involved in spreading false information about the 2022 Brazilian elections. False claims of fraud in that election culminated in an attempt by ousted President Bolsonaro’s supporters to spark a coup d’etat. In defiance of the TSE, Musk said he would reinstate those accounts; in response, Moraes announced he would include Musk in an investigation into the “digital militias” which contributed to the January 8th, 2022 riots which followed Bolsonaro’s loss. Musk ultimately relented. The accounts remained offline, and the platform formerly known as Twitter avoided a potential ban in one of its largest markets.
In the Brazilian context, Musk is perhaps best understood as a far-right variant of what the US government sometimes calls “malign foreign influence” (a term I have long disliked for its potentially xenophobic interpretations, despite the often good intentions of those that use it). Even when he plays the fool, Musk and his ilk should be considered with deadly seriousness.
Continue reading.
27 notes
·
View notes
Text
by Dion J. Pierre
The US House of Representatives has launched an investigation into 20 nonprofit organizations that are currently funding anti-Zionist student groups mounting pro-Hamas demonstrations on college campuses, an effort aimed at uncovering long suspected links to terrorist organizations and other hostile foreign entities.
As part of the inquiry, US Reps. Virginia Foxx (R-NC) and James Comer (R-KY) wrote to Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen on Tuesday, asking her to share any “suspicious activity reports” generated by the activities of Students for Justice in Palestine, Jewish Voice for Peace, American Muslims for Palestine, Tides Foundation, Rockefeller Brothers Fund, Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation, the Council on American-Islamic Relations, and other groups.
Foxx and Comer chair the House Committee on Education and the Workforce and the House Committee on Oversight and Accountability, respectively.
“The committees are investigating the sources of funding and financing for groups who are organizing, leading, and participating in pro-Hamas, antisemitic, anti-Israel, and anti-American protests with illegal encampments on American college campuses,” Foxx and Comer wrote in their letter to Yellen. “This investigation relates to both malign influence on college campuses and to the national security implications of such influence on faculty and student organizations.”
The inquiry comes amid widespread suspicion that an eruption of anti-Zionist protests on college campuses, in which students illegally occupied sections of section and refused to leave unless their schools agreed to condemn and boycott Israel, was fueled by immense financial and logistical support from outside groups. Foxx and Comer said in their letter that the investigation’s findings will inform recommendations for new federal laws requiring increased transparency and reporting of foreign contributions to American colleges and universities.
On Tuesday, Foxx told the Washington Free Beacon, which first reported the investigation, that the protests were a symptom of a larger threat to national security.
“It’s no coincidence that the day after the October 7 Hamas terrorist attack, antisemitic mobs began springing up at college campuses across the country,” Foxx said. “These protests have been coordinated and well organized, indicating that outside groups or influences may be at play. American education is under attack. It’s critical that Congress investigates how these groups — who are tearing apart our institutions — are being funded and advised before it’s too late.”
Foreign links to the anti-Zionist student movement have been the subject of numerous comprehensive studies.
Last week, the Network Contagion Research Institute (NCRI) published a report showing a connection between the anti-Zionist group Shut It Down for Palestine (SID4P) — a group formed immediately after Hamas’ massacre on Oct. 7 — and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). NCRI explained that SID4P, which organized numerous traffic-obstructing demonstrations after Oct. 7, is an umbrella group for several other organizations which compose the “Singham Network,” a consortium of far-left groups funded by Neville Roy Singham and Jodie Evans. The report describes Singham and Evans as a “power couple within the global far-left movement” whose affiliation with the CCP has been copiously documented.
“The Singham Network exploits regulatory loopholes in the US nonprofit system to facilitate the flow of an enormous sum of US dollars to organizations and movements that actively stoke social unrest at the grassroots level,” the report said. “Alternative media outlets associated with the Singham Network have played a central role in online mobilization and cross-platform social amplification for SID4P.”
In 2022, the National Association of Scholars (NAS) revealed that one of the founders of Students for Justice in Palestine, Hatem Bazian, is also a co-founder of American Muslims for Palestine, an advocacy group which, NAS said, “retains ties to terrorist groups operating in the Palestinian Territories.”
NAS added that the Palestinian Campaign for the Academic Cultural Boycott of Israel — which has been influential is steering the boycott, divestment, and sanctions (BDS) movement against Israel in academia — is “structurally linked” to Palestinian terrorist organizations through the Council of National and Islamic Forces in Palestine — a member of the Palestinian BDS National Committee which comprises Hamas, the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLP), Popular Front-General Command, Palestinian Liberation Front, and Palestinian Islamic Jihad.
“On the one hand, BDS is designed to secure political legitimacy vis-á-vis Israel, with boycotts and divestment offering Palestinian activists and terrorists new domains to assert their cause,” NAS senior fellow Ian Oxnevad wrote. “On the other hand, BDS, along with the formation of multiple NGOs and nonprofit organizations, offers the Palestinians new avenues by which to access funding in a post-9/11 international financial system designed to curtail funding for terrorism.”
#anti-zionists#protests#students for justice in palestine#bds#virginia fox#james comer#investigation
50 notes
·
View notes
Text
May 22 (UPI) -- Far-right Romanian presidential candidate George Simion lost a legal bid Thursday to annul last weekend's run-off election after a surprise loss to centrist rival, former Bucharest Mayor Nicusor Dan.
Romania's Constitutional Court threw out the challenge to the election result by Simion, who accused foreign states, including France, of vote-buying and alleging ballot fraud involving some of Nicusor's votes.
In a unanimous decision, the judges ruled Simion's request to annul the election was "unfounded" because the presidential poll complied with all "procedures within the scope of its authority," the court said.
Simion, leader of the Alliance for the Unity of Romanians party, attacked the decision, calling it a "coup" and urged his supporters to fight on.
Dan, who is an independent, condemned Simion's legal challenge as trumped up, saying "it was clear from the beginning to everyone that it was completely artificial."
The strategically key European Union country and NATO ally has been in unprecedented territory since the court annulled a presidential election in December, two days before a run-off between centrist Elena Lasconi and previously unknown far-right candidate Calin Georgescu, citing Russian interference.
Simion polled 40.96% of the vote in the rerun of the election earlier this month -- short of the 50% needed for an outright win -- but was expected to prevail over Dan in Sunday's run-off because the mayor received half as many votes.
Simion has previously argued against military assistance for Ukraine in its struggle to repel invading Russian forces and in favor of a return to the Greater Romania of the interwar years by reunifying Romania with neighboring Romanian-speaking Moldova.
Simion received a three-year entry ban from Ukraine in 2024 for "systematic anti-Ukrainian" activities and is also banned from neighboring Moldova on national security grounds.
The constitutional court's decision to annul "the entire electoral process" came after declassified Romanian intelligence files detailed a security services warning that Russia had attacked the election system with an "aggressive hybrid action" in order to promote Georgescu.
The intelligence assessment was that Georgescu's victory was "not a natural outcome," and that a "state actor" had enabled him to leap ahead of Lasconi and Prime Minister Marcel Ciolacu with an artificially coordinated social media campaign run from 25,000 TikTok accounts activated just two weeks before the first-round vote.
Condemning the alleged Russian interference, then-U.S. President Joe Biden said it was critical that Romanians had confidence their elections reflected the democratic will of the people "free of foreign malign influence aimed at undermining the fairness of their elections."
3 notes
·
View notes
Text

Billboard project
* * * * *
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
September 6, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Sep 07, 2024
One of the things that came to light on Wednesday, in the paperwork the Justice Department unveiled to explain its seizure of 32 internet domains being used by Russian agents in foreign malign influence campaigns, was that the six right-wing U.S. influencers mentioned in the indictments of the Russian operatives are only the tip of the iceberg.
Since at least 2022, three Russian companies working with the Kremlin have been trying to change foreign politics in a campaign they called “Doppelganger,” covertly spreading Russian government propaganda. “[F]irst and foremost,” notes from a meeting with Russian officials about targeting Germany read, “we need to discredit the USA, Great Britain, and NATO.” Through fake social media profiles, their operatives posed as Americans or other non-Russians, seeding public conversations with Russian propaganda.
In August 2023 they launched the “Good Old USA Project” to target swing-state residents, online gamers, American Jews, and “US citizens of Hispanic descent” to reelect Donald Trump. "They are afraid of losing the American way of life and the ‘American dream,’” one of the propagandists wrote. “It is these sentiments that should be exploited in the course of an information campaign in/for the United States.” Using targeted ads on Facebook, they could see how their material was landing and use bots and trolls to push their narrative in comment sections.
“In order for this work to be effective, you need to use a minimum of fake news and a maximum of realistic information,” the propagandists told their staff. “At the same time, you should continuously repeat that this is what is really happening, but the official media will never tell you about it or show it to you.”
According to the documents, one of the three companies, Social Design Agency (SDA), monitors and collects information about media organizations and social media influencers. It collected a list of 1,900 “anti-influencers,” whose accounts posted material SDA workers thought operated against Russian interests. About 26% of those accounts were based in the U.S.
SDA also identified as pro-Russian influencers more than 2,800 people in 81 countries operating on various social media platforms like X, Facebook, and Telegram. Those influencers included “television and radio hosts, politicians, bloggers, journalists, businessmen, professors, think-tank analysts, veterans, professors, and comedians.” About 21% of those influencers were in the U.S.
YouTube took down the Tenet Media Channels associated with the Justice Department’s indictments, and last night, Tenet Media abruptly shut down. In The Bulwark, Jonathan V. Last noted that the Tenet influencers maintain they were dupes, although they must have been aware that their paychecks were crazy high for the numbers of viewers they had. He asks if, knowing now that their gains are ill-gotten, they are going to give them to charity.
Earlier this week, former Fox News Channel personality Tucker Carlson hosted Holocaust denier Darryl Cooper on his X show, where Cooper not only suggested that the death of more than six million Jews was an accidental result of poor planning, but also argued that British prime minister Winston Churchill, who stood firm against the expansion of fascist Germany in World War II, was the true villain of the war.
Cooper’s argument puts him squarely on the side of Russian president Vladimir Putin and Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán, who insist that democracy undermines society. During the recent summer Olympics, Cooper posted on social media an image of Hitler in Paris alongside another of drag queens representing Greek gods at the Olympic opening ceremonies, an image some on the right thought made fun of the Last Supper of Jesus and his disciples. “This may be putting it too crudely for some,” Cooper wrote, “but the picture [of Hitler in Paris] was infinitely preferable in virtually every way than the one on the right.”
The idea that Churchill, not Hitler, is the villain of World War II means denying the fact of the Holocaust and defending the Nazis. It lands Carlson and Cooper in the same camp as those autocrats journalist Anne Applebaum notes are “making common cause with MAGA Republicans to discredit liberalism and freedom around the world.” Elon Musk promoted the interview, saying it was “very interesting,” and “worth watching,” before the backlash made him delete his post. The video has been viewed nearly 30 million times.
Carlson told Lauren Irwin of The Hill that the Biden administration is made up of “warmonger freaks” who have “used the Churchill myth to bring our country closer to nuclear war than at any moment in history.” Carlson is on a 16-day speaking tour, on which he will interview Trump allies, including Republican vice presidential nominee J.D. Vance and Donald Trump Jr.
Trump today continued his effort to undermine the democratic American legal system in a “news conference” of more than 45 minutes, in which he took no questions. Although Judge Juan Merchan, who oversaw the election interference case in which a jury found Trump guilty on 34 counts, decided today to delay sentencing until November 26 to avoid any appearance that the court was trying to affect the 2024 election, Trump nonetheless launched an attack on the U.S. legal system and suggested the lawsuits against him were election interference.
He spoke after he and his legal team were in court today to try to overturn a jury’s conclusion that he had sexually assaulted writer E. Jean Carroll, a decision that brought his judgments in the two cases she brought to around $90 million. He began with an attack on what he said was a new “Russia, Russia, Russia” hoax, and promised he had not “spoken to anybody from Russia in years.”
Aaron Rupar of Public Notice recorded what amounted to close to an hour of attacks on the American Justice Department and the laws of the country, and also on American women (he not only attacked Carroll, he brought up others of the roughly two dozen women who have accused him of sexual assault). He attempted to retry the Carroll case in the media, refuting the evidence the jury considered and suggesting that the photo of him and Carroll together was generated by AI, although it was published in 2019.
Attacking women was an interesting decision in light of the fact that he will need the votes of suburban women if he is to make up the ground he has lost to Democratic presidential nominee Vice President Kamala Harris and vice presidential nominee Tim Walz.
For her part, former representative Liz Cheney (R-WY) appears to see this moment for what it is. Although a staunch Republican herself, she is urging conservative women to admit they’ve had enough. Referring to both Trump and Vance in a conversation sponsored by the Texas Tribune, she said: “This is my diplomatic way of saying it: They’re misogynistic pigs.” She assured listeners, quite accurately, that Trump “is not a conservative.” “Women around this country…we’ve had enough.” “These are not people that we can entrust with power again.”
Her father, former vice president Dick Cheney, agreed that Trump “can never be trusted with power again” and announced today that he will be voting for Harris. “As citizens, we each have a duty to put country above partisanship to defend our Constitution. That is why I will be casting my vote for Vice President Kamala Harris,” he said. Eighty-eight business leaders also endorsed Harris today, including James Murdoch, an heir to the Murdoch family media empire. Citing Harris’s “policies that support the rule of law, stability, and a sound business environment,” they said in a public letter, “the best way to support the continued strength, security, and reliability of our democracy and economy” is by electing Harris president.
Meanwhile, at his event with Sean Hannity of the Fox News Channel yesterday, Trump embraced the key element of Project 2025 that calls for a dictatorial leader to take over the U.S. That document maintains that “personnel is policy” and that the way to achieve all that the Christian nationalists want is to fire the nonpartisan civil servants currently in place and put their own people into office. Trump has tried hard to distance himself from Project 2025, but last night he said the way to run the government is to “get the right people. You put the right person and the right group of people at the heads of these massive agencies, you’re going to have tremendous success, and I know now the people, and I know them better than anybody would know them.”
One of those people appears to be X owner Elon Musk, whom Trump has promised to put at the head of an “efficiency” commission to audit the U.S. government.
In 1858, Abraham Lincoln, then a candidate for the Senate, warned that the arguments against democracy and in favor of a few people dominating the rest were always the same. In his era, it was enslavers saying some people were better than others. But, he said, those were the same arguments “that kings have made for enslaving the people in all ages of the world…. Turn in whatever way you will—whether it come from the mouth of a King, an excuse for enslaving the people of his country, or from the mouth of men of one race as a reason for enslaving the men of another race, it is all the same old serpent.”
In our era, Indiana Jones said it best in The Last Crusade: “Nazis. I hate these guys.”
LETTERS FROM AN AMERICAN
HEATHER COX RICHARDSON
#Tenet Media channels#Letters From An american#Heather Cox Richardson#Indiana Jones#Abraham Lincoln#democracy#authoritarianism#Russian Propaganda#social media
14 notes
·
View notes
Text
Editor's note: This article is part of the “Monitoring the pillars of democracy” series. It focuses on the seven pillars essential to defending democracy, as outlined in the Brookings Democracy Playbook 2025 published by the Anti-Corruption, Democracy, and Security (ACDS) project. The series includes research and commentary on actionable steps democracy actors can take to strengthen democratic institutions and protect freedoms in the U.S. and abroad.
Since the Trump administration took office, the U.S. went from one of the world’s leading champions of fighting corruption to what risks being the opposite, with far-reaching costs to the American people at home and globally. We wrote about the need to prioritize fighting corruption as a key pillar of defending American democracy in the Democracy Playbook 2025 and how, if unchecked, corruption can advance autocracy.
It is deeply concerning how quickly the Trump administration is undermining critical U.S. anti-corruption frameworks and leadership globally. These actions run counter to bipartisan efforts undertaken by previous administrations and the U.S. Congress to fight illicit finance and malign foreign influence to protect American interests from corrupt actors. These actions also stand in contrast to the recognition of the harms associated with illicit finance and other corruption issues, as noted in resources such as the Trump administration’s U.S. Intelligence Community’s 2025 Annual Threat Assessment.
Many of the administration’s recent actions, including the disbanding of anti-corruption bodies and the absence or limited enforcement of existing laws, could have short- and long-term negative impacts on the health, employment, safety, and security of many Americans. However, businesses, policymakers, civil society, media, and citizens have tools at their disposal to defend against what may be a devastating wave of corruption and other threats to democratic governance.
In this article, we highlight several key corruption threats; potential security, economic, and other impacts; and pathways for Americans and other stakeholders to act both individually and collectively to counter anti-corruption rollbacks. We recognize that there are other acute challenges, including the threat of state capture, abuse of power, and rise of American oligarchs, that deserve thorough attention. We will continue to examine these other growing areas of corruption risks, and pathways for addressing them, as we continue our series of analysis on threats to American democracy.
15 notes
·
View notes
Text
September 6, 2024
Heather Cox Richardson
Sep 07, 2024
One of the things that came to light on Wednesday, in the paperwork the Justice Department unveiled to explain its seizure of 32 internet domains being used by Russian agents in foreign malign influence campaigns, was that the six right-wing U.S. influencers mentioned in the indictments of the Russian operatives are only the tip of the iceberg.
Since at least 2022, three Russian companies working with the Kremlin have been trying to change foreign politics in a campaign they called “Doppelganger,” covertly spreading Russian government propaganda. “[F]irst and foremost,” notes from a meeting with Russian officials about targeting Germany read, “we need to discredit the USA, Great Britain, and NATO.” Through fake social media profiles, their operatives posed as Americans or other non-Russians, seeding public conversations with Russian propaganda.
In August 2023 they launched the “Good Old USA Project” to target swing-state residents, online gamers, American Jews, and “US citizens of Hispanic descent” to reelect Donald Trump. "They are afraid of losing the American way of life and the ‘American dream,’” one of the propagandists wrote. “It is these sentiments that should be exploited in the course of an information campaign in/for the United States.” Using targeted ads on Facebook, they could see how their material was landing and use bots and trolls to push their narrative in comment sections.
“In order for this work to be effective, you need to use a minimum of fake news and a maximum of realistic information,” the propagandists told their staff. “At the same time, you should continuously repeat that this is what is really happening, but the official media will never tell you about it or show it to you.”
According to the documents, one of the three companies, Social Design Agency (SDA), monitors and collects information about media organizations and social media influencers. It collected a list of 1,900 “anti-influencers,” whose accounts posted material SDA workers thought operated against Russian interests. About 26% of those accounts were based in the U.S.
SDA also identified as pro-Russian influencers more than 2,800 people in 81 countries operating on various social media platforms like X, Facebook, and Telegram. Those influencers included “television and radio hosts, politicians, bloggers, journalists, businessmen, professors, think-tank analysts, veterans, professors, and comedians.” About 21% of those influencers were in the U.S.
YouTube took down the Tenet Media Channels associated with the Justice Department’s indictments, and last night, Tenet Media abruptly shut down. In The Bulwark, Jonathan V. Last noted that the Tenet influencers maintain they were dupes, although they must have been aware that their paychecks were crazy high for the numbers of viewers they had. He asks if, knowing now that their gains are ill-gotten, they are going to give them to charity.
Earlier this week, former Fox News Channel personality Tucker Carlson hosted Holocaust denier Darryl Cooper on his X show, where Cooper not only suggested that the death of more than six million Jews was an accidental result of poor planning, but also argued that British prime minister Winston Churchill, who stood firm against the expansion of fascist Germany in World War II, was the true villain of the war.
Cooper’s argument puts him squarely on the side of Russian president Vladimir Putin and Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán, who insist that democracy undermines society. During the recent summer Olympics, Cooper posted on social media an image of Hitler in Paris alongside another of drag queens representing Greek gods at the Olympic opening ceremonies, an image some on the right thought made fun of the Last Supper of Jesus and his disciples. “This may be putting it too crudely for some,” Cooper wrote, “but the picture [of Hitler in Paris] was infinitely preferable in virtually every way than the one on the right.”
The idea that Churchill, not Hitler, is the villain of World War II means denying the fact of the Holocaust and defending the Nazis. It lands Carlson and Cooper in the same camp as those autocrats journalist Anne Applebaum notes are “making common cause with MAGA Republicans to discredit liberalism and freedom around the world.” Elon Musk promoted the interview, saying it was “very interesting,” and “worth watching,” before the backlash made him delete his post. The video has been viewed nearly 30 million times.
Carlson told Lauren Irwin of The Hill that the Biden administration is made up of “warmonger freaks” who have “used the Churchill myth to bring our country closer to nuclear war than at any moment in history.” Carlson is on a 16-day speaking tour, on which he will interview Trump allies, including Republican vice presidential nominee J.D. Vance and Donald Trump Jr.
Trump today continued his effort to undermine the democratic American legal system in a “news conference” of more than 45 minutes, in which he took no questions. Although Judge Juan Merchan, who oversaw the election interference case in which a jury found Trump guilty on 34 counts, decided today to delay sentencing until November 26 to avoid any appearance that the court was trying to affect the 2024 election, Trump nonetheless launched an attack on the U.S. legal system and suggested the lawsuits against him were election interference.
He spoke after he and his legal team were in court today to try to overturn a jury’s conclusion that he had sexually assaulted writer E. Jean Carroll, a decision that brought his judgments in the two cases she brought to around $90 million. He began with an attack on what he said was a new “Russia, Russia, Russia” hoax, and promised he had not “spoken to anybody from Russia in years.”
Aaron Rupar of Public Notice recorded what amounted to close to an hour of attacks on the American Justice Department and the laws of the country, and also on American women (he not only attacked Carroll, he brought up others of the roughly two dozen women who have accused him of sexual assault). He attempted to retry the Carroll case in the media, refuting the evidence the jury considered and suggesting that the photo of him and Carroll together was generated by AI, although it was published in 2019.
Attacking women was an interesting decision in light of the fact that he will need the votes of suburban women if he is to make up the ground he has lost to Democratic presidential nominee Vice President Kamala Harris and vice presidential nominee Tim Walz.
For her part, former representative Liz Cheney (R-WY) appears to see this moment for what it is. Although a staunch Republican herself, she is urging conservative women to admit they’ve had enough. Referring to both Trump and Vance in a conversation sponsored by the Texas Tribune, she said: “This is my diplomatic way of saying it: They’re misogynistic pigs.” She assured listeners, quite accurately, that Trump “is not a conservative.” “Women around this country…we’ve had enough.” “These are not people that we can entrust with power again.”
Her father, former vice president Dick Cheney, agreed that Trump “can never be trusted with power again” and announced today that he will be voting for Harris. “As citizens, we each have a duty to put country above partisanship to defend our Constitution. That is why I will be casting my vote for Vice President Kamala Harris,” he said. Eighty-eight business leaders also endorsed Harris today, including James Murdoch, an heir to the Murdoch family media empire. Citing Harris’s “policies that support the rule of law, stability, and a sound business environment,” they said in a public letter, “the best way to support the continued strength, security, and reliability of our democracy and economy” is by electing Harris president.
Meanwhile, at his event with Sean Hannity of the Fox News Channel yesterday, Trump embraced the key element of Project 2025 that calls for a dictatorial leader to take over the U.S. That document maintains that “personnel is policy” and that the way to achieve all that the Christian nationalists want is to fire the nonpartisan civil servants currently in place and put their own people into office. Trump has tried hard to distance himself from Project 2025, but last night he said the way to run the government is to “get the right people. You put the right person and the right group of people at the heads of these massive agencies, you’re going to have tremendous success, and I know now the people, and I know them better than anybody would know them.”
One of those people appears to be X owner Elon Musk, whom Trump has promised to put at the head of an “efficiency” commission to audit the U.S. government.
In 1858, Abraham Lincoln, then a candidate for the Senate, warned that the arguments against democracy and in favor of a few people dominating the rest were always the same. In his era, it was enslavers saying some people were better than others. But, he said, those were the same arguments “that kings have made for enslaving the people in all ages of the world…. Turn in whatever way you will—whether it come from the mouth of a King, an excuse for enslaving the people of his country, or from the mouth of men of one race as a reason for enslaving the men of another race, it is all the same old serpent.”
In our era, Indiana Jones said it best in The Last Crusade: “Nazis. I hate these guys.”
—
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Ken Klippenstein:
It all started with Hamas’ October 7, 2023 attack on Israel and concerns about anti-Semitic content on the social media platform TikTok. It all ended with a classified briefing and a foolish attempt, still alive, to ban the social media platform. The company’s ownership by China never was the driving force in Congress eventually taking action. This week at the Munich Security Conference, Sen. Mark Warner, the top Democrat on the intelligence committee, played “I’ve got a secret.” It’s a game national security officialdom loves to play, slyly claiming authority ‘if they could only tell you what they know.’ It is in that vein that Warner spilled the beans on what he called the “real story” behind the law that could still ban TikTok. “I want to see if you're going to tell the real story,” a grinning Warner said, addressing former congressman Mike Gallagher, and now a Palantir executive who, along with Warner, first introduced the bill that claimed that TikTok was a national security threat, a claim still relevant given the app’s uncertain future. Gallagher described how the national security bill was dead until Hamas’ attack on Israel, which brought the legislation back to life.
The account by Gallagher makes explicit something there have been hints of for some time. Israeli officials and lobbyists told everyone that would listen in Washington that TikTok’s algorithm fueled American youth opposition to the Israel-Hamas war. As I reported last year, a State Department source told me that a high-ranking Israeli diplomat was ranting about the supposed malign role of some Chinese-manufactured algorithm, purposely dismissive of the reality that the college protesters’ outrage was sincere, that it was about Israel’s military conduct in Gaza and not some “foreign malign influence” campaign hatched in Beijing. NPR at about the same time reported on a memo written by Israel Foreign Ministry Deputy Director General Emmanuel Nahshon, which blamed TikTok’s algorithm for “turning young people against Israel.”
[...] So the “real story” is pretty simple. Congress chose to take action essentially to suppress speech and protect Israel. The Biden administration hid behind China in its justification as to why a ban was essential. The classified briefing — still secret — did the dirty work. “Conspired” indeed, as Gallagher said. They’ve got a secret. They always do. And that leaves nothing for the public to push back on, which is the true conspiracy.
Turns out that the TikTok ban signed into law by former President Biden was predicated over concerns about “anti-Israel” content.
#TikTok Ban#TikTok#Israel#China#Munich Security Conference#Mike Gallagher#Mark Warner#Israel/Hamas War#Gaza Genocide#Mitt Romney#Sara Jacobs
6 notes
·
View notes
Text
Moon of Alabama January 31, 2025
A few days ago the Trump administration put a 90 day stop on foreign aid:
Friday’s memo shocked the humanitarian groups and communities conducting development aid across the globe. While the scope of the directive appears far-reaching, uncertainties linger over how it will be carried out.
The memo on Saturday offered only partial clarity.
The pause on foreign aid spending means “a complete halt,” it said. The only exceptions are for emergency humanitarian food assistance and for government officials returning to their duty stations. Waivers allowing delivery of emergency food during the review period will require “detailed information and justification.” … USAID began sending a notice to contractors ordering them to “immediately issue stop-work orders” and to “amend, or suspend existing awards.”
USAID and other U.S. government entities provide money for a wide range of causes. Some are arguably humanitarian and should continue:
Trump order set to halt supply of HIV, malaria drugs to poor countries as part of aid freeze, sources say – NY Post, Jan 28 2025
Others though are not so.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Heard a woman unironically say that she has turned to reading the National Review, a site called (I think) The Christian Monitor or something, and watching Fox News because, “No one else cares about antisemitism” in regards to the violence in Israel-Palestine.
And I was like… you did not turn to a Conservative Christian news site for a nuanced understanding of antisemitism. You turned to these outlets for confirmation of your Islamophobia. You could have easily turned to NPR, who just today interviewed two Rabbis to discuss how Jewish communities process and handle grief.
The National Review recently claimed that standing for Israel is standing for “western values.” I want to ask you: since when have the people who scream about the degradation of such things as “Judaeo-Christian values” or cry about attacks on “Western values” ever been *not* antisemitic and racist?
Fox News employs Greg Gutfeld, the man who said that Jewish people “had to be useful” to the Nazis to survive the Holocaust. The network frequently platforms men like Joe diGenova, who on Nov. 13, 2019 got onto the “Lou Dobbs Tonight” on the Fox Business Network, and maligned progressive activist George Soros, a Jewish man. DiGenova claimed that Soros controls the Foreign Service and State Department, and that he is a corrupting influence on the U.S. government. Col. Douglas MacGregor got onto the same show and claimed “Soros in particular has funded or helped fund these massive migrations out of Central America.” He described Soros as having tentacles. Plus, former host Tucker Carlson also frequently accused Soros of using his wealth to change American society and also lionized Henry Ford, the man who inspired Adolf Hitler and published the anti-Semitic screed, The International Jew.
Fox News is WELL KNOWN for being one of the many reasons for rises in antisemitism in the United States. They are a contributing factor. Why would you go to a well known antisemitic network for “unbiased” reporting on Israel? You’re only going to be exposed to vile antisemitic propaganda. Like, if this is where you’re going for non-antisemitic news, you’re going to be sorely disappointed.
The reason you’ve found yourself drawn to these media networks for their coverage of Israel is because they confirm for you that which you want to hear about Arab people and Palestinian Liberation as these same networks are also well known for their Islamophobia and for contributing to Islamophobic violence in the US, most recently with the stabbing of a 6 y/o boy in the Chicagoland.
Let’s be real here. No one legitimately turns to notorious antisemites for non-antisemitic news. You’re looking for the religious bigotry and racism they peddle.
18 notes
·
View notes